Table of contents
Working directory
In your work directory, create a directory ~/PHY432/03_python and go to this directory:
mkdir ~/PHY432/03_python
cd ~/PHY432/03_pythonPython Hello World program
Using you favorite editor (for instance, Visual Studio Code, i.e., the code command), create a text file named hello.py in the directory ~/PHY432/03_python1 with the following content:
# hello world in Python
name = input("What's your name? --> ")
print("Hello ", name, ", it's great to see you here.")Execute (“run”) your hello.py program with the python program:
python hello.pyIt should ask you for your name: type it and hit Enter. You should be greeted nicely with a message on your screen.
- The line starting with
#is a comment and Python ignores everything on the line starting with the comment character. - Blank lines are ignored.
nameis a variable: it stores a value (more later); variable names are arbitrary (as long as you only use letters, numbers, underscore, don’t start with a number, and don’t use a name that is already used by Python)input()andprint()are functions: they take values as input and do something with it (more later).
What’s a Python program?
A text file with content that follows the rules of the Python programming language.
Customarily, we add the suffix
.pyto the filename, but this is not required.The text file is read by the
pythoninterpreter (a program) and executed.
Python interpreter
Python is an interpreted language; you can think of python reading each line in an input file and executing it. Start python on its own:
pythonYou should see something like
Python 3.8.11 (default, Aug 3 2021, 05:10:14)
[Clang 10.0.0 ] :: Anaconda, Inc. on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
The Python prompt is >>>.
Type commands and execute them with Enter. Like the shell, Python is a REPL, a “Read-eval-print-loop”. For example, to add two numbers
>>> 41 + 1
42
>>> 1.5 + 5e-1
2.0Exit with quit() or Ctrl + d.
Help!
In Python you can often get help by saying
>>> help()
>>> help("something")For example, get help on the addition operator (and much more):
>>> help("+")Exercise Python as a calculator
Start python and figure out 2 how to compute the left hand sides (the right hand sides are there for you to check your results):
More operations
- floor division (“integer division”)
//3 - remainder
%
>>> 13 / 3 # division returns a float
4.333333333333333
>>> 13 // 3 # floor division discards the fractional part
4
>>> 13 % 3 # the % operator returns the remainder of the division
1
>>> 4 * 3 + 1 # result * divisor + remainder
13Potential problems…
Division by zero raises an error (an “exception”):
>>> 1/0
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ZeroDivisionError: division by zeroFloating point numbers are not real real numbers (more later): calculating \(10 + 10^{-16} = 10.0000000000000001\) in Python
>>> 10 + 1e-16
10.0does not give the expected answer!
Exercise hello, line by line
Type the commands from hello.py into the interpreter, hitting Enter after every line, and execute your program step by step.
Basic plotting
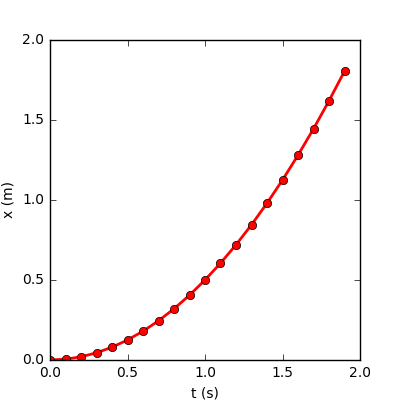
Create a file motion.py with content
# plot motion with constant acceleration
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a = 1.0 # acceleration
v0 = 0.0 # initial velocity
t, h, n = 0.0, 0.1, 20 # init time, step size, number of steps
ta, xa = [], [] # time and position lists
for i in range(n):
x = v0*t + a*t*t/2.0
ta.append(t)
xa.append(x)
t = t + h
# plot results
plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
plt.plot(ta, xa, '-o', color="red", linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("t (s)")
plt.ylabel("x (m)")
plt.savefig("motion.png")
plt.show()You should create a graph similar to the following:
Interactive Python with ipython
The ipython interpreter is like python but with lots of improvements such as TAB-completion, help with command? (one question mark directly following a command) and source code with command?? (two question marks), command line history, and many additional shell-like commands (so-called “magic” commands such as %cd, %ls, %pwd, %run, %time and %timeit — see %magic for help).
Start it with
ipythonIt should look like
Python 3.8.11 (default, Aug 3 2021, 05:10:14)
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 7.12.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]:
where In [1]: is the prompt.
Use ipython instead of python for interactive work because it is much more userfriendly.
ipython basics
- To exit, give the
exit()command or^D(Control+D). - Use arrow keys to move up and down through the history or through multi-line commands.
- Use TAB-completion.
- Use
command?or?command(question mark directly before or after a command or object) to get help %run FILEexecutes FILE similarly topython FILE.4
ipython with matplotlib
In the basic plotting example we used the matplotlib library for plotting and wrote a figure to a file. ipython can show figures interactively but the details depend on your operating system and installed packages. Try the following and see if the figure is displayed on your screen when you run motion.py: 5
Windows
Run jupyter qtconsole to show graphics inline (this used to be called ipython qtconsole):
jupyter qtconsoleIn ipython 4
%run motion.pymacOS
Run ipython
ipythonIn ipython 4
%run motion.pyTroubleshooting:
- If the above does not show a graph, try running
ipython --matplotlib=osx. - Alternatively,
jupyter qtconcolewill likely also work (with inline graphs).
Linux
Run ipython
ipython --matplotlib=gtk3(If gtk3 does not work, try qt5, qt, wx, tk, auto, or just --matplotlib.)
In ipython 4
%run motion.pyFootnotes
If you can call your editor from the command line then this is as easy as, for example with
code(ornano),cd ~/PHY432/03_python code hello.pyThis will open a new file with name
hello.pyor open an existing file if it is present.However, if you use an editor that you have to open from, say, the Windows Start menu, then you need to first open the editor and then use a menu command such as File → New to create a blank document (use or File → Open to open an existing file). Once you have written content you need to save it in the correct location (usually, or File → Save). To find the
03_pythondirectory, first navigate to your home directory:This can be tricky on Windows : In your shell (not in your editor), type
cd; pwdto learn the path to your home directory. In your editor’s file system dialog window, start from the system disk (normallyC:under Computer) and look forC:\Users\YOUR_USERNAME.On Apple Mac OS X, your home directory is
/Users/YOUR_USERNAME.On typical Linux distributions it is
/home/YOUR_USERNAME.
In your home directory, locate the
PHY432folder, click on it to find the03_pythonfolder inside and click on the latter. Provide the file name (“hello.py”) and save the file. (In the shell, make sure that the file is in place where you expect it to be, i.e.,ls -la.) ↩If you need help, look at Using Python as a Calculator in the standard Python Tutorial. ↩
In Python 2, the
/division operator would perform floor division if both operands were integers but normal (“true”) division if at least one operand was a floating point number. Therefore, in old Python 2 code you might see constructs such as1.0 * a / 2to force a true division, no matter the value of the variablea. In Python 3, the/operator always performs true division, which prevents some rather nasty bugs from occuring. ↩%runis an ipython “magic” command, see help on those commands with%magic. ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4If you don’t want to see graphics inline but as a separate window you can try
ipython --matplotlib=qt5(If
qt5does not work, tryqt,wx,tk,auto, or just--matplotlib.)However, this does not always work and might require additional packages. Please share any insights and solutions! ↩